CONTENT
- Nomenclature
- Preparation
- Properties
- Uses.
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
These are hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms join with each other by multiple bonds. The multiple bond can be double bonds e.g Alkene or triple bonds e.g Alkyne.
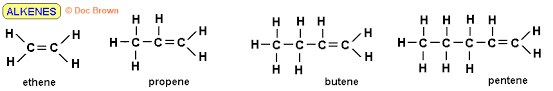
Nomenclature
The process of naming in alkene is obtained by substitute “ane” in alkane with ‘ene’ e.g Ethane changes to Ethene, propane to prepene
Physical Properties
1. Ethene is a colourless gas with faint sweetish odour .
2. It is sparingly soluble in water
3. It is slightly less dense than air
4. It has no action on litmus paper
Evaluation
1. Write four (4) physical properties of Ethene
2. How would you prepare a jar of ethane gas in the laboratory?
USES
- Used in the manufacture of plastics.
- Used in making synthetic rubber.
- Used to hasten the ripening of fruits.
- Used in the production of other organic compounds e.g halo-alkane,ethane, ethanol.
Evaluation
1. Describe the reaction of ethane with the following:
- Bromine water
- Chlorine water
- Acidified KMnO4
- State four (4) uses of Ethene.
READING ASSIGNMENT
New School Chemistry by O.Y. AbabioPg 459-492
Theory
1. Describe two (2) methods of obtaining ethene industrially.
2a. Write and name the geometric isomers of compound with the molecular formular C5H10
b. With chemical equation only, show how ethane reacts with the following:
– ozone
– oxygen
– alkaline KMnO4
– Conc. H2SO4
Read our disclaimer.
AD: Take Free online baptism course: Preachi.com