REFRACTION THROUGH TRIANGULAR AND RECTANGULAR PRISM
Triangular prism
When a ray of light passes through a triangular prism, it is refracted as shown below
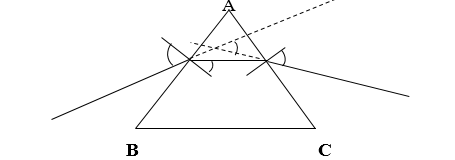
Angle of deviation
The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is known as the angle of deviation. The angle of deviation decreases as the angle of incidence increases
The refractive index, n=sin (A/2+D/2)/sin A/2
Rectangular prism
Real and apparent depth
A thick slab of glass appears to be only two –third of its real thickness when viewed vertically from above. Similarly, water in a pond appears to be only three quarters of its real depth. Rays from a coin at the bottom of a bucket of water are refracted away when they leave water and enter the eyes. They appear as if coming from a virtual image, which is apparent depth while the actual depth of the bottom remains and is referred to as real depth
Refractive index=real depth/apparent depth
CLASSWORK 1
ASSIGNMENT 1
SECTION A
Use the information below to answer questions 7, 8 and 9
The angle of incidence of a narrow beam of light on a side of an equilateral triangular prism is 480. Calculate the:
SECTION B
Read our disclaimer.
AD: Take Free online baptism course: Preachi.com 