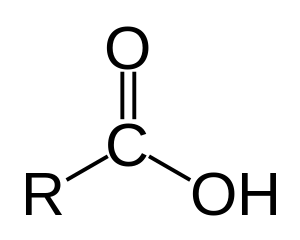
Alkanoic Acids
Alkanoic acids are also known as carboxylic acids. A carboxylic acid can he identified from the carboxyl functional group and the ‘-oic’ name ending.
| Formula | longest carbon chain | C-C single bonds | functional group | Name | occurrence |
| HCOOH | C1 : meth | -an- | -COOH (oic acid) | methanoic acid (formic acid) | ants |
| CH3COOH | C2 : eth | -an- | -COOH (oic acid) | ethanoic acid (acetic acid) | vinegar |
| C2H5COOH | C3 : prop | -an- | -COOH (oic acid) | propanoic acid (propionic acid) | dairy products |
| C3H7COOH | C4 : but | -an- | -COOH (oic acid) | butanoic acid (butyric acid) | rancid butter |
| C4H9COOH | C5 : pent | -an- | -COOH (oic acid) | pentanoic acid (valeric acid) | valerian root |
General formula of carboxylic (alkanoic acids) : CnH2n+1COOH or R-COOH
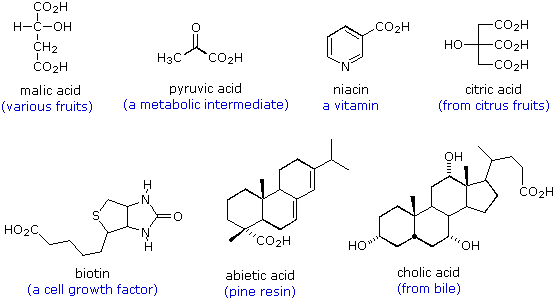
Examples of Carboxylic (Alkanoic) Acids
Nomenclature (Naming Alkanoic Acids)
Alkanoic acids are named as follows:
For example:
methylpentanoic
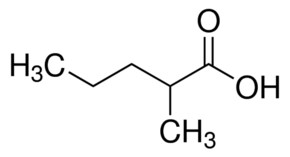
2-ethylpentanoic acid
benzoic acid

The Complete Oxidation of Ethanol to Ethanoic Acid by acidified sodium heptaoxochromate(VI) solution. Ethanol undergoes oxidation first to ethanal and then to ethanoic acid.
The reaction of sodium dichromate(VI) solution with ethanol gives a carboxylic acid, ethanoic acid, a dilute solution of which is sold as vinegar.
Ethanoic acid can also be prepared by
CH3COONa(aq)+ H2SO4(aq) → CH3COOH(g) + NaHSO4 (aq)
CH3CN(aq) + HCl(aq) → CH3COOH(g) + NH4Cl(aq)
Physical Properties
Chemical Properties of Carboxylic (Alkanoic) Acids
Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization: acid + base → salt + water
Carboxylic (alkanoic) acid + base → salt (metal alkanoate) + water
RCOOH + MOH → RCOO–M+ + H2O
e.g. CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COO–Na+ + H2O
Ethanoic acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium ethanoate + water
Soluble salts of long-chain (fatty) acids are soaps
e.g. C17H35COOH + NaOH → C17H35COO–Na+ + H2O
Stearic acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium stearate + water
Reaction with Carbonates
acid + carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide gas + water
Carboxylic (alkanoic) acid + metal carbonate → metal alkanoate + carbon dioxide + water
e.g. 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COO–Na+ + CO2 + H2O
Ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium ethanoate + carbon dioxide + water
e.g. CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COO–Na+ + CO2 + H2O
Ethanoic acid + sodium bicarbonate → sodium ethanoate + carbon dioxide + water
Reaction with Active Metals
Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen gas
Carboxylic (alkanoic) acid + metal → metal alkanoate + hydrogen
e.g. 2CH3COOH + 2Na(s) → 2CH3COO–Na+ + H2(g)
Ethanoic acid + sodium → sodium ethanoate + hydrogen
Esterification Reactions
Esters are produced in a condensation reaction between a carboxylic (alkanoic) acid and an alkanol (alcohol).
This is known as an esterification reaction.
carboxylic (alkanoic) acid + alkanol (alcohol) ester + water
e.g. 2CH3COOH + CH3OH CH3COOCH3 + H2O
Ethanoic acid + methanol methyl ethanoate + water
Uses
Assessment
It is used in food industries as vinegar for preserving and flavouring food. True/False
Read our disclaimer.
AD: Take Free online baptism course: Preachi.com 