Nitrogen, which makes up about 78% of our atmosphere, is a colorless, odorless, tasteless and chemically unreactive gas at room temperature. It is named from the Greek nitron + genes for soda forming. For many years during the 1500’s and 1600’s scientists hinted that there was another gas in the atmosphere besides carbon dioxide and oxygen. It was not until the 1700’s that scientists could prove there was in fact another gas that took up mass in the atmosphere of the Earth.
Daniel Rutherford, a Scottish Physician, discovered Nitrogen in 1772. But it was Lavoisier, who proved that nitrogen is an element and that it was not a supporter of combustion and respiration. He called it ‘azote’ meaning ‘no life’. The name ‘Nitrogen’ was given to it by Jean Antoine Chaptal (1756 – 1832), in the year 1790.
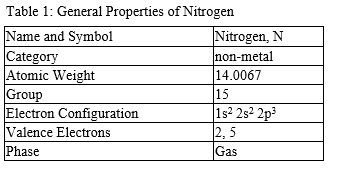
Nitrogen is found to have either 3 or 5 valence electrons and lies at the top of Group 15 on the periodic table. It can have either 3 or 5 valence electrons because it can bond in the outer 2p and 2s orbitals. Nitrogen is not reactive at standard temperature and pressure. Nitrogen is a colorless, and odorless gas that is usually found in its molecular form of (N2). For the most part, Nitrogen is inert.
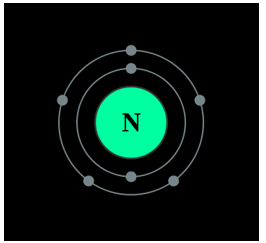
A Bohr diagram of the nitrogen atom.
Nitrogen is a non-metal element that occurs most abundantly in the atmosphere, nitrogen gas (N2) comprises 78.1% of the volume of the Earth’s air. It only appears in 0.002% of the earth’s crust by mass. Compounds of nitrogen are found in foods, explosives, poisons, and fertilizers. Nitrogen makes up DNA in the form of nitrogenous bases as well as in neurotransmitters. It is one of the largest industrial gases, and is produced commercially as a gas and a liquid.
Isotopes
Nitrogen has two naturally occurring isotopes, nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15, which can be separated with chemical exchanges or thermal diffusion. Nitrogen also has isotopes with 12, 13, 16, 17 masses, but they are radioactive.
The chief source of free nitrogen is atmospheric air and nitrogen is usually prepared from it. Air free from dust, water vapour and carbon dioxide is compressed in a compression chamber for liquefaction.
Firstly, the pressure on the air is increased to about 200 atmospheres. It is then released through a spiral into a low-pressure area, where intense cooling of the air takes place.
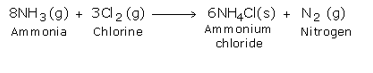
By treating excess ammonia with chlorine, ammonium chloride and nitrogen are formed.
In the laboratory, nitrogen is prepared by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite and a small quantity of water. If ammonium nitrite is heated by itself, it decomposes to produce nitrogen gas. However, this reaction is very fast and may prove to be explosive
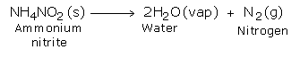
Combination with elements. Nitrogen does not easily combine with other elements under ordinary conditions. A molecule of nitrogen is diatomic. These two atoms have combined by mutually sharing three pairs of electrons.
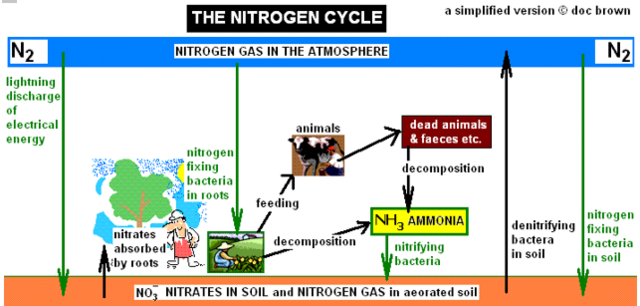
.The Nitrogen Cyclefor the gaseous element N2(g)
EVALUATION
1.Describe the physical and chemical properties of Nitrogen.
2.With the aid of a well labelled diagram,describe the preparation of Nitrogen from air
3.Describe the Laboratory preparation of a named Hydride.
4.Give an example of a reaction in which ammonia behaves as a i.reducing agent ii.base iii.precipitating agent
post your answers to the forum for review
Read our disclaimer.
AD: Take Free online baptism course: Preachi.com 