CONTENT
- Magnets and its Properties.
- Magnetization and Demagnetization.
- Temporary and Permanent Magnets.
- Magnetic Flux.
- Earth Magnetic Field.
MAGNET AND ITS PROPERTIES
A magnet is any material that is capable of attracting other pieces of the same material as well as pieces of iron.Lodestone is an iron ore which has the property of attracting pieces of iron’s substance is said to be ferromagnetic if it is attracted by a magnet. Examples are iron,cobalt,Nickel,and certain alloys. Substances which cannot be attracted by a magnet are called non magnetic material e.g brass, wood, copper, and glass.
PROPERTIES OF MAGNETS
1.The ends of a magnet where the attracting power is greatest are called the poles.
2. A bar magnet suspended freely in a vertical plane called magnetic meridian comes to rest with its axis in the North-South direction. The part which points northwards is called the north seeking pole or North pole while the opposite pole is called the south pole
3.Like poles of magnet repel each other while unlike poles attract each other.
4. The polarity of a magnet can be tested by bringing both poles in turn nearer to the known pole of a suspended magnet. Repulsion indicates similar polarity. Attraction could be due to two unlike poles or a pole and a piece of unmagnetized material.Hence, repulsion is the only sure test for polarity.
MAGNETIZATION AND DEMAGNETIZATION
Magnetization is a process whereby a material is made to become magnetic. This can be achieved through any of the following methods.
ELECTRICAL METHOD
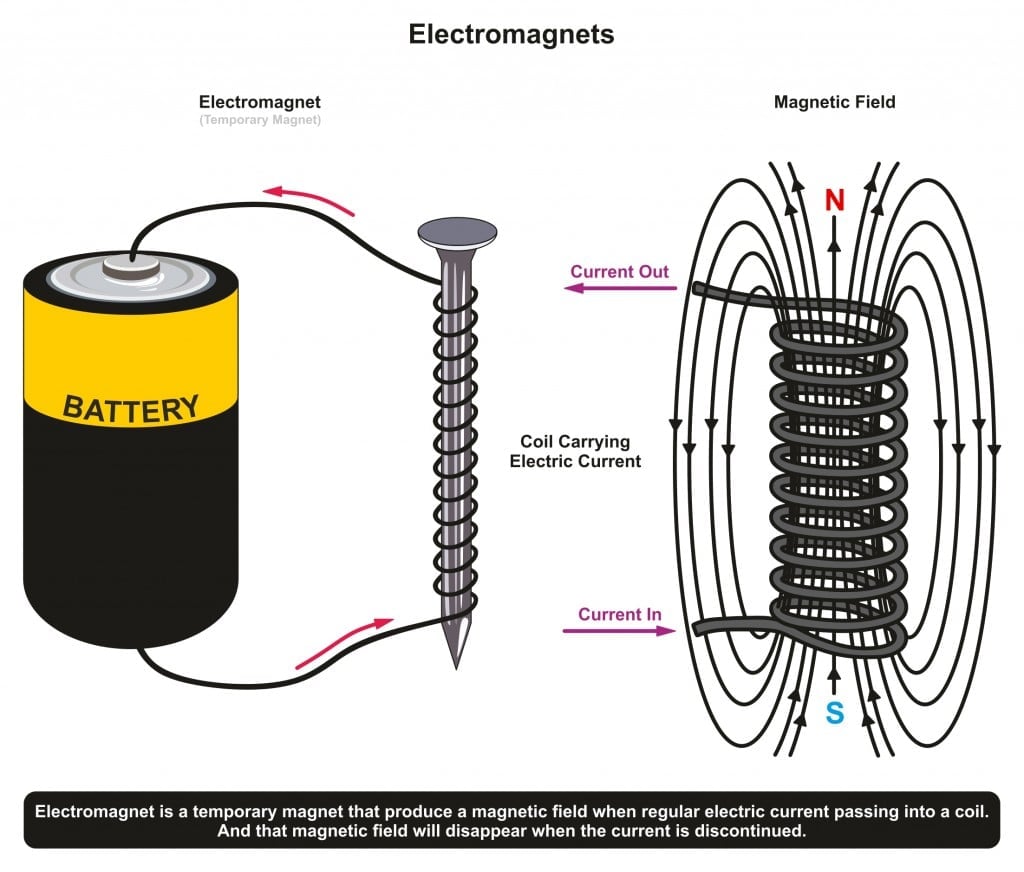
A cylindrical coil wound with several turns of insulated copper wire is connected in series with a six or twelve volt electric battery and switch.A coil of this type is called a solenoid.A steel bar is placed inside the coil and the current is switched on for sometime. On removing and testing the steel, it will be found to have been magnetized. It is unnecessary to leave the current for long as length of time makes no difference but causes over heating. The induce polarity depends on the direction of flow of the current. Clockwise flow at an end indicates South Pole while an anti-clockwise flow indicates North Pole.
SINGLE TOUCH METHOD
A steel bar is stroke from end to end several times in the same direction with a known pole of a magnet. Between successive strokes the pole is lifted high above the bar otherwise the magnetism already induced will be weakened. The disadvantage of this method is that it produces magnets in which one pole is nearer the end of the bar than the other.
DIVIDED TOUCH METHOD
Here the steel bar is stroke from the centre outward with unlike poles of two magnets simultaneously. The polarity produced at the end of the bar where the stroking finishes is of opposite kind to that of the stroking pole.

HAMMERING IN THE EARTH FIELD
Magnets can be made by hammering red hot steel bar and allow it to cool as it lies in North- South direction.
INDUCED MAGNETISM
When a piece of unmagnetized steel is placed either near or in contact with a pole of a magnet and then removed, it will be magnetized. This is called Induced Magnetism. The induced pole is of opposite sign to that of inducing pole.
DEMAGNETIZATION
This is a process whereby a magnet is made to lose its magnetism. Demagnetization can be achieved by:
- ELECTRICAL METHOD
The magnet is placed in a solenoid through which an alternating current is flowing. The solenoid is placed with its axis pointing in the East Westdirection. After a few seconds, the magnet is slowly withdrawn out of the solenoid to a long distance away. This is the most efficient way of demagnetizing a magnet.
- MECHANICAL METHOD
Another method of demagnetizing magnets is to hammer it hard when it is pointing in the East West direction.
- HEATING METHOD
When magnet is strongly heated, it loses its magnetism.
EVALUATION
- With the aid of a diagram, explain the following methods of magnetization: electrical, single and divided touch.
- What is the demerit of using the method of divided touch?.
TEMPORARY AND PERMANENT MAGNET
Soft iron is pure iron while steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. Steel is a much harder and stronger material than soft iron. Steel and iron have different magnetic properties.
Iron is easily magnetized than steel but it readily loses its magnetism. Steel produces a stronger magnet, which is the reason why steel is used for making permanent magnet such as compass needle. In temporary magnets, where the magnetism is required for a short time, iron is used,e.g electromagnets.
EVALUATION
- Differentiate between steel and iron with respect to magnetism.
- What are magnets and how can you differentiate between a magnetic and non magnetic material?
MAGNETIC FIELDS
Magnetic field is the space surrounding the magnets in which magnetic force is exerted. It is a vector quantity and it is represented by magnetic lines. The direction of the magnetic flux at any point is the direction of the force on a north pole placed at that point.
In the neighbourhood of two magnets placed closed together, there exist a field in which the direction of the magnetic flux changes rapidly in a confined space. The magnetic flux can be obtained by using iron fillings.
Magnetic meridian at any place is a vertical plane containing the magnetic axis of a freely suspended magnet at rest under the action of the earth field.The geographical meridian at a place is a plane containing the place and the earth axis of rotation.
The angle between the magnetic and geographical meridian is called the Magnetic Declination.The angle of dip or inclination is the angle between the direction of the earth magnetic flux and the horizontal.
EVALUATION
With the aid of a suitable diagram, explain the following.Magnetic Flux, Angle of Inclination andAngle of Declination.
READING ASSIGNMENT
New School Physics for Senior Secondary Schools (M.W. ANYAKOHA Pages 425—430).
GENERAL EVALUATION
- A gas occupies a certain volume at 270C.At what temperature would the volume be three time the original volume assuming constant pressure.
- A gas with initial volume 2X 106 m3 is allowed to expand six times its original volume at constant pressure of 2X 105 N/m2, what is the work done?
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
- An iron ore which attracts pieces of iron to itself is called —(A) iron (B) steel (C) lodestone (D) cobalt
- The following are magnetic substances except —(A) cobalt (B) Nickel (C) iron (D) brass
- The end of a solenoid where current flow is clockwise represents—(A) north pole (B) neutral pole (C) south pole (D) magnetic equator
- A magnetic substance can be demagnetized by —(A) dropping on the floor. (B) hammering while red hot. (C) divided touch. (D) single touch.
- The following are alloys for making powerful magnets except —(A) alcomax (B) alnico (C) mumeta(D) ticonal
THEORY
- Explain the term magnetic fields
- State and explain three properties of a magnet.
Read our disclaimer.
AD: Take Free online baptism course: Preachi.com 