Soil formation is greatly controlled by five major factors which are (i) Climate (ii)Parent materials (iii) topography (iv) biotic (living organism) (v) time
Rainfall enhances vegetative growth of plants whose roots cause further breakdown of rocks, while the rain water transports rock particles after disintegration.
PROCESS OF SOIL FORMATION
The process of soil formation is called weathering. Weathering is defined as the disintegration or breakdown of rocks into tiny pieces to form soil. In other words, weathering can also be defined as the breaking down of rock masses (rock minerals) into simpler forms through the agents of physical, chemical and biological processes.
The Processes of soil formation include:
COMPOSTION (COMPONENTS OF THE SOIL)
The soil is made up of five components which are (i) In-organic (mineral) matter (ii) Organic water (iii)soil water (iv) soil air (v)living organisms.
Mineral or inorganic matter, organic matter, water and air are collectively referred to as physical components of the soil while living organisms are refered to as biological components of the soil.
Importance/Effects of Mineral Matter on Agriculture
Importance /Effects of Organic Matter on Agriculture
Types of Soil Water
There are four major types of soil water. These are:
Importance/Effects of Soil water on Agriculture:
Importance /Effects of Soil Air on Agriculture
Importance/Effects of Living Organisms on Agriculture
Soil organisms are very useful in many ways, especially in soil-formation and improving the soil for the growth of crops. Their effects are:
SOIL TYPES AND THEIR PROPERTIES
Definition of Soil: Soil is defined as the uppermost layer of the earth’s crust which provides support and nutrients for plant growth.
There are three main types of soil. These are sandy soil, clay soil, and loamy soil.
Sandy Soil: Soil is said to be sandy if the proportion of sand particles in a sample of the soil is very high. The particles are mainly quartz (SiOz) and having a size of 0.02mmm to 2.0mm in diameter.
Properties of Sandy Soil
Methods of Improving Sandy Soil
Sandy soil can be improved throughout the following agricultural practices:
Economic importance of Sandy Soil
Clay soil
Definition: Soil is said to be clayey if the proportion of clay in a sample of the soil is very high. The relative size of clay particle is less than 0.002mm in diameter. It is a heavy type of soil because it is difficult to work on or cultivate.
Properties of Clay soil.
Note: Clay soil can be improved through (i) liming (ii) addition of organic manure.
Loamy Soil
Definition: Loamy soil is a mixture of sand and clay particles with high proportion of organic matter. Loamy soil is more fertile than either clay or sandy soil. If a type of soil is described as sandy loam, it means that the proportion of sand is high and if it is clay loam, it shows that the proportion of clay is high, while that of sand is low.
Properties of Loamy soil
Importance/Effects of Organic Matter on Agriculture
Properties of the Soil
Properties of the soil include soil texture, soil structure, soil temperature, porosity, soil colour, water-holding/retaining capacity and soil pH.
The properties of the soil are grouped into two:
SOIL PROFILE
Soil profile is defined as the vertical section of the soil, showing series of horizontal layers of different types of soil. These horizontal layers are called horizons.
A soil profile in an area of the humid tropics such as the forest zones may have about four fairly distinct horizons. The first thing that is noticed in a soil profile is soil colour. The horizons show different colours, e.g., the top soil may be dark, followed by brown below.
After the colour, the next feature which can be noticed is the texture or particle sizes which increase from the top to the bottom. These two characteristics enable the different horizons to be identified.
Horizons of Soil Profile
The four major horizons of soil profile are:
Importance of Soil Profile
The suitability of a soil for agriculture is determined by looking at the soil profile. The importance of soil profile includes:
SOIL TEXTURE
Definition: Soil texture refers to the relative proportion (sizes) of the various particles of the soil. In other words, it refers to the degree of fineness or coarseness of the various soil particles.
The particles that make up a soil sample include gravel, sand, silt and clay. Silt and clay are usually referred to as the primary particles of the soil.
The name and sizes of the various soil particles are shown in the table below.
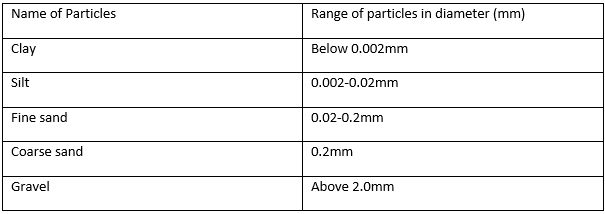
Determination of Soil Texture
Soil texture can be determined by various methods. These methods include:
Importance of Soil Texture
Soil texture is very important, especially to farmers in the following ways:
Soil structure
Soil structure refers to the way in which the different particles of the soil are packed or arranged. It also refers to the shape and arrangement of primary particles form compound particles.
Soil structure has a direct effect on crop yield. If the soil structure is good, air will circulate well while waterlogging, erosion and leaching will be reduced. The structure of the soil can be preserved in the following ways.
Types of Soil Structure
The different types of soil structure are:
Importance of soil structure
Soil Temperature
Soil temperature refers to the temperature within the soil. In other words, it is the temperature usually different from the temperature of the air above the soil.
Soil pH
The word of pH (pondus de Hydronium) is defined as a measure of the degree of acidity or alkalinity of the soil. It can also be described as a measure of the concentration of hydrogen (H+) in the soil. A higher hydrogenions (H+) concentration indicates soil acidity while a lower concentration of hydrogen ions (OH+) indicates soil alkalinity.
Causes of Soil Acidity
Soil acidity can be caused by any of the following:
Removal of Soil Acidity
Soil acidity can be removed by the application of liming materials which are rich in calcium.
Examples of liming materials include:
Questions:
Read our disclaimer.
AD: Take Free online baptism course: Preachi.com 